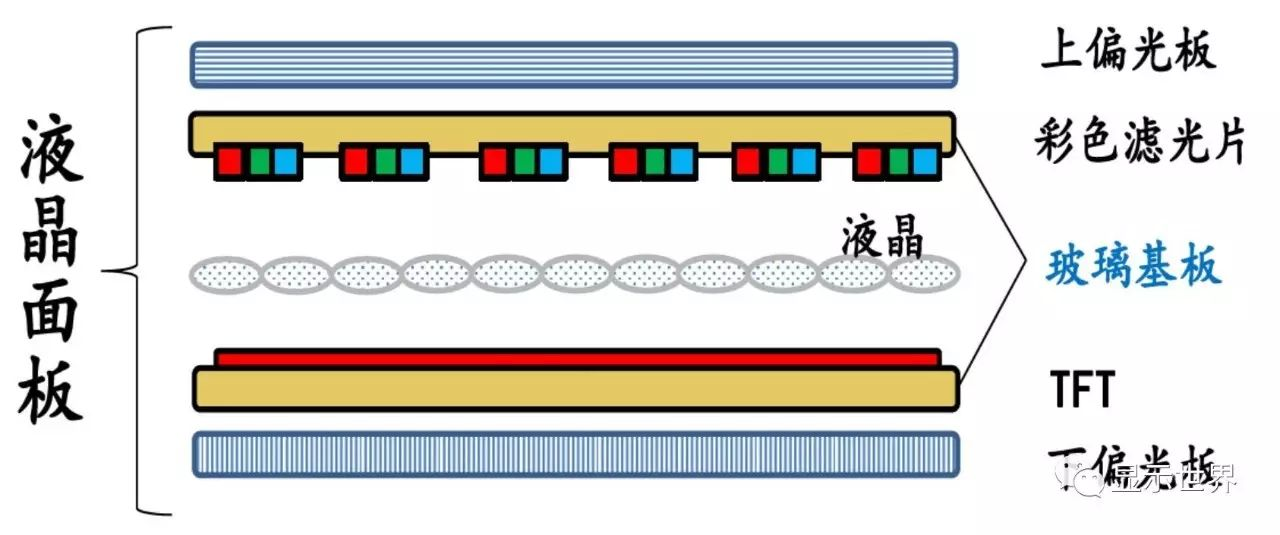
Substrate glass is one of the important raw materials for liquid crystal panel. The key structure of the LCD panel is similar to a sandwich, with two layers of "bread" (TFT substrate and color filter) and "jam" (liquid crystal). Therefore, two pieces of glass are needed to make a TFT-LCD panel, which are used as the bottom glass substrate and color filter substrate respectively.
Substrate glass accounts for about 20% of the cost of TFT-LCD raw materials, which has a huge impact on the performance of panel products. The resolution, transmittance, thickness, weight, visual angle and other indicators of panel products are closely related to the quality of substrate glass used. As an important substrate, the significance of substrate glass to TFT-LCD industry is equivalent to that of silicon wafer to semiconductor industry.
TFT-LCD panel structure
Substrate glass is one of the important raw materials for liquid crystal panel. The key structure of the LCD panel is similar to a sandwich, with two layers of "bread" (TFT substrate and color filter) and "jam" (liquid crystal). Therefore, two pieces of glass are needed to make a TFT-LCD panel, which are used as the bottom glass substrate and color filter substrate respectively.
Substrate glass accounts for about 20% of the cost of TFT-LCD raw materials, which has a huge impact on the performance of panel products. The resolution, transmittance, thickness, weight, visual angle and other indicators of panel products are closely related to the quality of substrate glass used. As an important substrate, the significance of substrate glass to TFT-LCD industry is equivalent to that of silicon wafer to semiconductor industry.
TFT-LCD panel structure
Substrate glass is one of the important raw materials for liquid crystal panel. The key structure of the LCD panel is similar to a sandwich, with two layers of "bread" (TFT substrate and color filter) and "jam" (liquid crystal). Therefore, two pieces of glass are needed to make a TFT-LCD panel, which are used as the bottom glass substrate and color filter substrate respectively.
Substrate glass accounts for about 20% of the cost of TFT-LCD raw materials, which has a huge impact on the performance of panel products. The resolution, transmittance, thickness, weight, visual angle and other indicators of panel products are closely related to the quality of substrate glass used. As an important substrate, the significance of substrate glass to TFT-LCD industry is equivalent to that of silicon wafer to semiconductor industry.
TFT-LCD panel structure
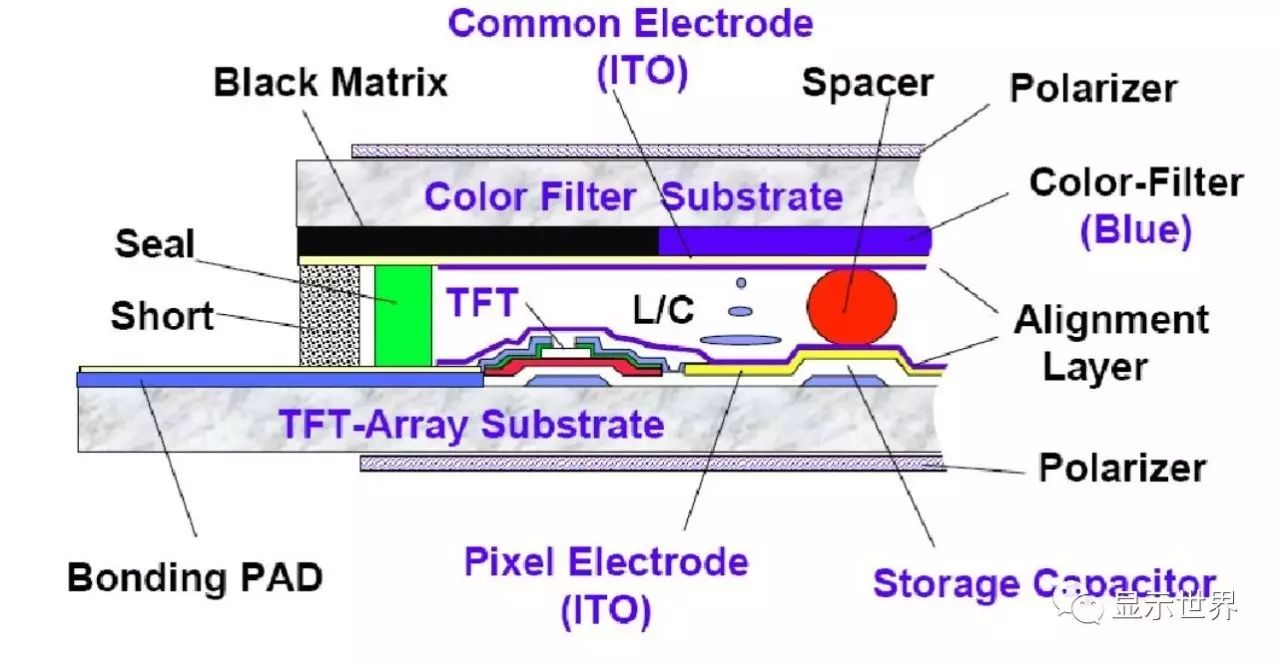
Base plate glass is divided into alkali containing and alkali free. Alkali glass is mainly used in TN / STN type liquid crystal panel, but for TFT-LCD, alkali metal ions in the glass will affect the stability of the gate voltage of thin film transistor, so the base plate must be manufactured with alkali free formula, and can not contain sodium oxide, potassium oxide and other components; however, sodium oxide and potassium oxide can reduce the melting temperature of the glass, so the manufacture of alkali free glass requires higher furnace temperature It is also one of the reasons why the production technology of non alkali glass is more difficult than that of alkali glass.
TFT-LCD LCD industry chain
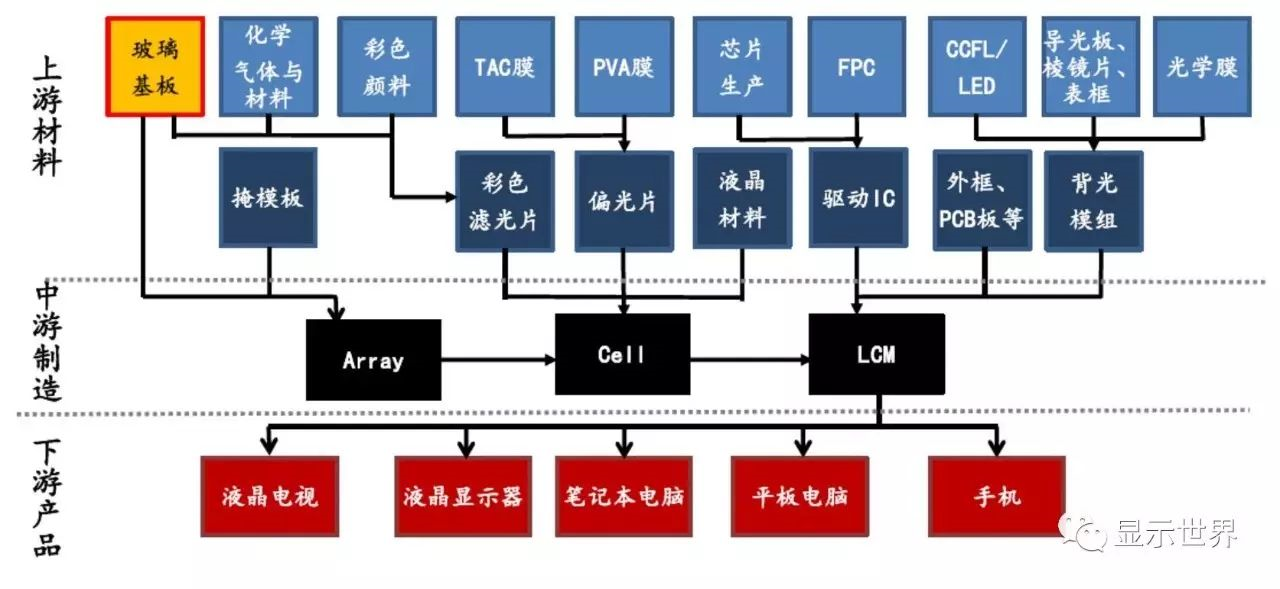
As one of the basic raw materials of LCD panel, substrate glass occupies the top of LCD industry chain. The upstream raw materials are some of the most basic chemical raw materials, such as quartz powder, alumina, etc., while the downstream are mainly panel factories and color filter suppliers, who are respectively supplied to make TFT arrays and color filters, and then fill liquid crystals and assemble them in the box forming section to make open cell panels.
Substrate glass supply chain

As the cornerstone of thin film display industry, substrate glass is not only widely used in TN / STN, TFT and other liquid crystal panel structures, but also an essential substrate material for OLED. The importance of substrate glass is limited by the change of display mechanism, which is irreplaceable and has a stable industrial position in the future.
Introduction to the characteristics of substrate glass
chemical properties
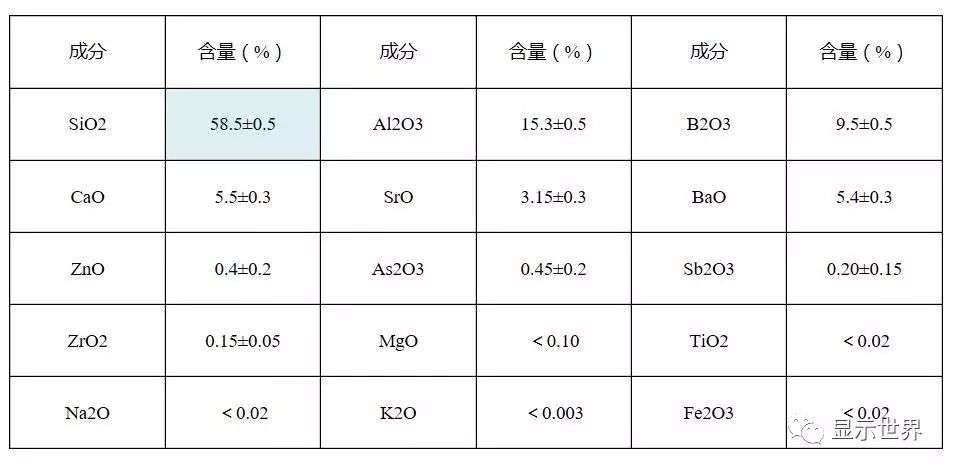
Main physical and chemical parameters
(1) Strain point
In the process of TFT manufacturing, the substrate needs repeated geothermal treatment, and the temperature should be heated to 625 ℃, which requires the substrate to remain rigid at this temperature, without any viscous flow phenomenon, otherwise, not only the glass deformation and cooling will bring thermal stress, but also the size change. Therefore, it is required that the strain point of the substrate glass is higher than 625 ℃, plus the insurance amount of 25 ℃, and the strain point of the glass is at least 650 ℃.
(2) Chemical stability
The substrate glass must be able to withstand all kinds of chemical treatment in the manufacturing process of the display, such as & alpha; - Si active matrix, LCD with more than 7 layers of thin film circuit and the same number of corrosion steps, corrosive and cleaning agent strong acid to strong alkali, such as more than 10% NaOH, more than 10% H2SO4, concentrated HNO3, 10% hf-hno3, concentrated H3PO4, etc., it can be said that the substrate almost requires the chemical stability of the glass The strictest of the varieties.
(3) Limitation of alkali
Because of the requirement of printed circuit on substrate glass, glass can not contain monovalent alkali metal, that is, R2O content is as low as possible, or even 0. Once the glass contains monovalent alkali metal, the monovalent alkali metal will overflow from the inside of the glass to the surface of the glass at high temperature, resulting in short circuit or fault of the printed circuit, etc., therefore, the monovalent alkali metal ions are strictly prohibited in the liquid crystal substrate glass.
Monovalent alkali metal, where the alkali metal (R2O) refers to monovalent alkali metal ions, mainly including K +, Na, Li.
(4) Coefficient of thermal expansion
In the manufacture of liquid crystal panel, a layer of silicon needs to be plated on the surface of glass, so the thermal expansion coefficient of glass must match with silicon, and the glass must have a thermal expansion coefficient close to silicon, and the expansion coefficient of silicon oxide is 5-7 & times; 10 / ℃.
On the other handBecause the display has to be heated and cooled many times, repeatedly and rapidly in the manufacturing process, it will inevitably cause the glass structure to relax and the size to change, which will make the electronic circuit of the photolithography plate deviate. Therefore, it is required that the shrink size of the whole substrate element is only a fraction of the thinnest width in the circuit diagram, i.e. a few microns. Low thermal shrinkage is still a necessary condition.
Generally speaking, the expansion coefficient of substrate glass is less than 40 times; 10 / ℃ in the temperature range of 0-300 ℃.
Glass raw materials and characteristics
The main raw materials of liquid crystal substrate glass include: quartz powder, strontium carbonate, barium carbonate, boric acid, borohydride, alumina, calcium carbonate, barium nitrate, magnesium oxide, tin oxide, zinc oxide, etc. They are the formation of glass, the regulator and intermediate components of glass, which constitute the main body of glass and determine the physical and chemical properties of this kind of glass.
Quartz flour
The main component of quartz powder is SiO2, which is the main oxide to form glass. It forms irregular continuous network with the structure of SiO4 tetrahedron, and becomes the skeleton of glass.
SiO2 can reduce the thermal expansion coefficient and density of glass, and improve the strain point of glass. When the content of SiO2 is too low, it will reduce the chemical stability of glass, such as acid resistance. It is not easy to obtain glass with low expansion, low density and high strain point, which makes it difficult to melt the glass and easy to cause stone (cristobalite) defects.
alumina
Alumina is an intermediate oxide. When the o in the glass is insufficient, the coordination number of Al is 6, which is in the network gap and forms [alo6] octahedron with O; when there is excess o in the glass, the coordination number of Al is 4, which enters the glass network and forms [alo4] tetrahedron with O, which plays a role of mesh filling, increases the glass stability and reduces the glass expansion coefficient. At the same time, due to the large volume of [alo4] tetrahedron, it can Reduce glass density. Al2O3 can significantly improve the strain point, elastic modulus and chemical stability of glass.
The content of silica and alumina is dependent on each other. The sum of the two should be more than 70% of the total raw materials.
Boric acid (boric anhydride)
Boric acid is used as a flux. Boric acid can reduce the melting viscosity of glass without increasing the expansion coefficient. A proper amount of boric oxide can increase the hydrofluoric acid resistance and make it easy to process. However, when the concentration of boric oxide is too high, the acid resistance of glass will be damaged and the strain point will be too low.
B in glass mainly forms boroxidation triangle [BO3] with O. if there is enough o in glass, tetrahedron [bo4] can be formed to reduce the thermal expansion coefficient of glass.
Boron oxide can reduce the melting point and facilitate the melting. But it also reduces the transition temperature, and is very harmful to chemical durability, so the boron oxide content is better below 10%.
Because the main content of boric anhydride is easily affected by moisture in the production process, the main control index of boric anhydride is the main content and moisture content. Generally speaking, in the process of use, attention should be paid to the moisture-proof in the warehouse and drying in the bin.
Strontium carbonate
Strontium carbonate is mainly introduced into strontium oxide. Strontium oxide has the characteristics of not increasing the density, not increasing the coefficient of linear expansion, not reducing the strain point too much, but also improving the solubility. If the content is too much, it will lead to the deterioration of the permeability, the acid resistance and the durability of the anti alkali, anti-corrosion film stripping solution. Strontium oxide can also absorb X-ray.
Zinc oxide
In general, zinc oxide octahedron [ZnO 6] is used as the external oxide of the network. When the free oxygen in the glass is enough, zinc oxide tetrahedron [ZnO 4] can be formed and enter the structure network of the glass, making the structure of the glass more stable. ZnO 4 can reduce the coefficient of thermal expansion and improve the chemical stability, thermal stability and refractive index of glass.
Tin oxide
Tin oxide is a kind of raw material to replace arsenic oxide as clarifier.
Mainstream technology of substrate glass manufacturing
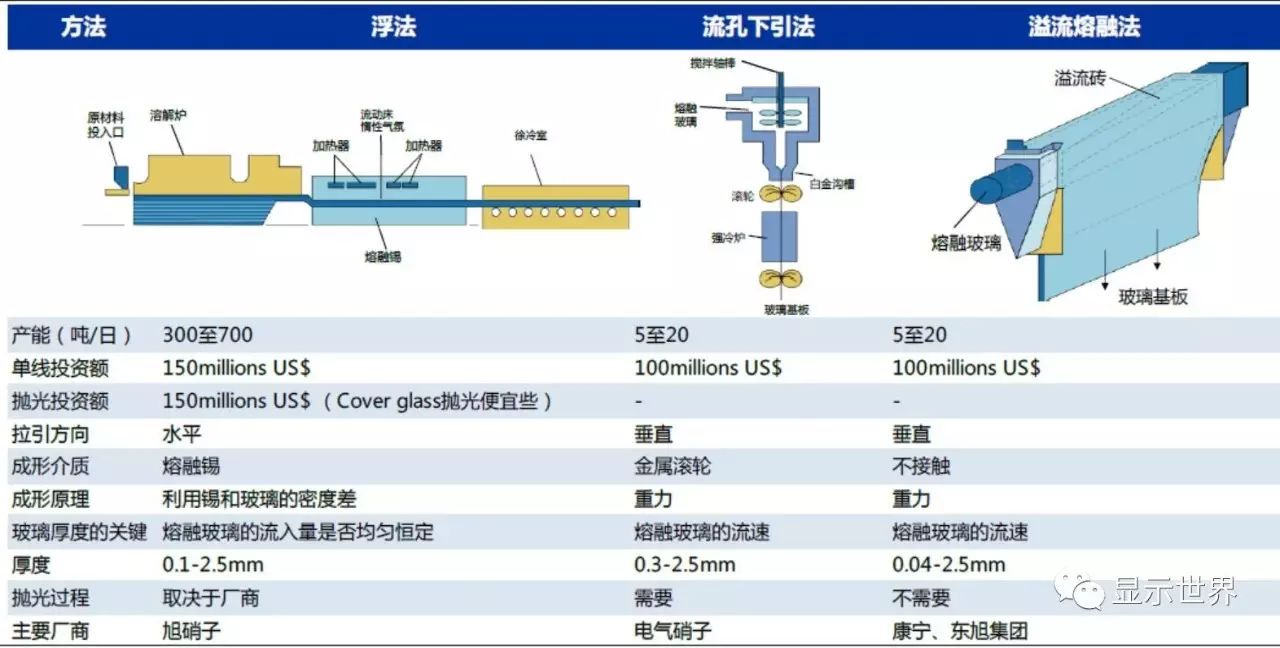
The manufacturing process of substrate glass mainly includes float method, flow hole down drawing method and overflow melting method. At present, the mainstream process is overflow melting method.
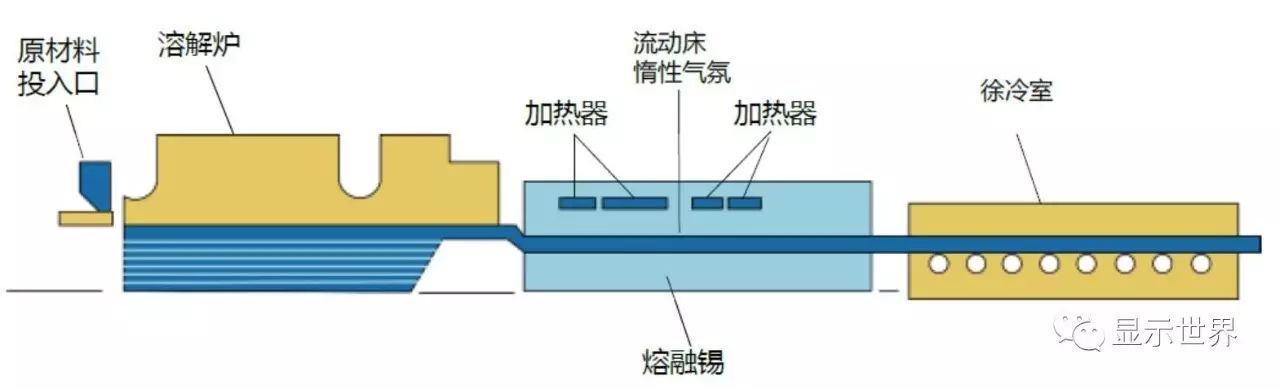
The float process is the most widely used and the oldest plate glass manufacturing process. In this method, the molten glass liquid is transferred to the groove containing molten tin. The density difference between tin and glass is used to flatten the liquid glass under the action of surface tension and gravity, and then it enters the cooling chamber for cooling and forming. Float glass needs further grinding, polishing and other processing. The advantages of float method are high production capacity, easy to expand the glass area of the substrate, and the cost is lower than that of other processes, but the cost of post-processing offsets some of the cost advantages. The float method was mainly used for TN / STN substrate glass before, and then Asahi successfully used float method to manufacture alkali free substrate glass, becoming the representative manufacturer of float method to manufacture TFT substrate glass.
Schematic diagram of float process
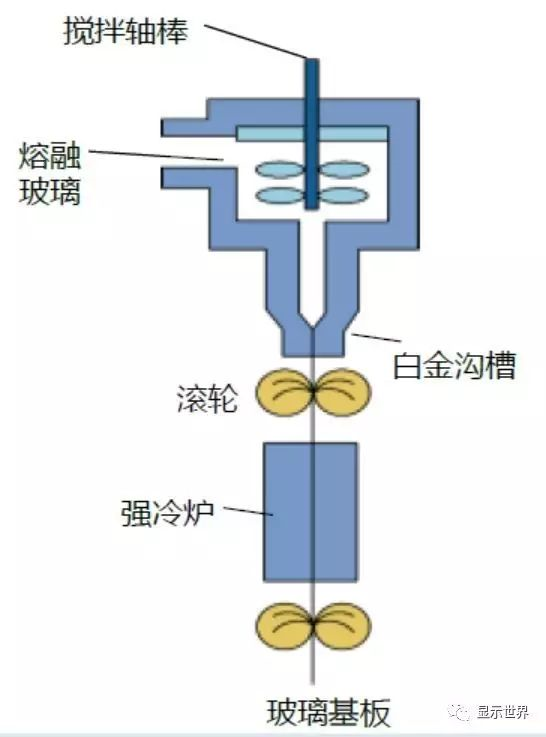
The flow hole pull-down method is to guide the molten glass liquid into the flow hole leakage plate groove of the platinum alloy process, under the action of gravity, the glass solution flows out, and then is rolled by the roller and solidified in the cooling chamber. The thickness of glass depends on the size of flow hole and downdraft speed, and the flatness of glass depends on the temperature distribution. The flow hole plays an important role in this process. Its size stability is related to the key indicators such as whether the thickness of glass is uniform or not, and whether the surface is flat or not. However, due to the effect of external forces, the flow hole may deform, and the yield will fluctuate. In addition, due to the contact between the glass surface and the roller, the flatness will also be affectedTherefore, this flow hole pull-down method also needs post polishing. The main manufacturer using this process is electrical nitrate. However, at present, due to the advantage of this process is not obvious, it has been gradually eliminated.
Schematic diagram of flow hole pull-down method
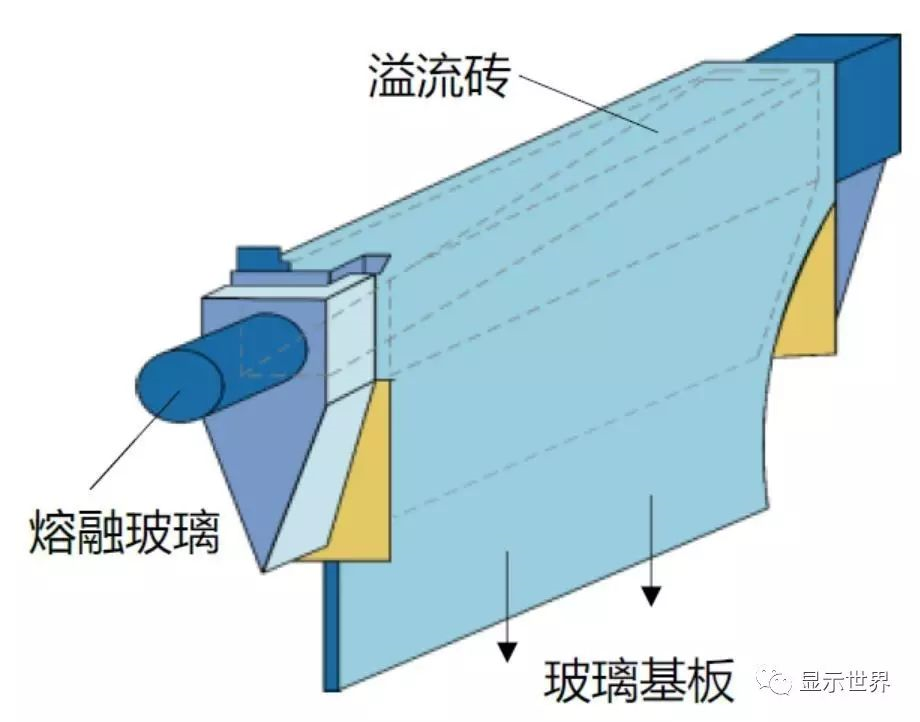
The overflow melting method is to guide the molten glass liquid into the conduit. When the glass liquid reaches the upper limit of the volume, it overflows from both sides of the conduit along the pipe wall and then flows out. Like a waterfall, it converges at the bottom to form a flaky substrate. The overflow melting method is dominated by Corning, a famous glass manufacturer. Because this process glass does not need to contact any medium (float method contacts liquid tin, flow hole method contacts metal roller) when forming, it will not cause the difference of glass surface properties caused by contact with the medium, so it does not need finishing and other processing. Now it has become the mainstream of TFT-LCD substrate glass manufacturing process 。
Schematic diagram of overflow melting method
Forming process
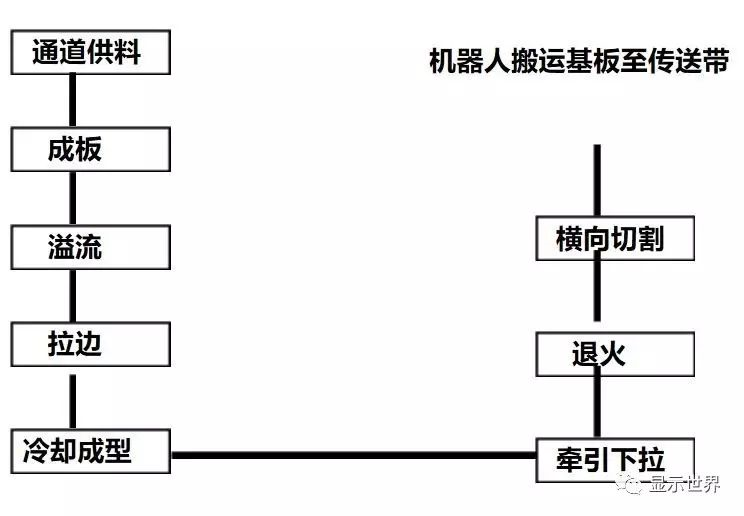
The forming process is to melt the pool furnace and clear, homogenize and cool down the glass liquid through the platinum channel, overflow the overflow brick in the muffle furnace, cool and cool down the forming area, use the annealing furnace to remove the product stress, and finally carry out transverse cutting, weighing, longitudinal cutting, thickness inspection, application inspection, electrostatic dust removal and external for the glass plate with flat surface and uniform thickness After the visual inspection, send the semi-finished substrate glass to the BOD (semi-finished product processing) process.
Comparison of three kinds of substrate glass manufacturing processes
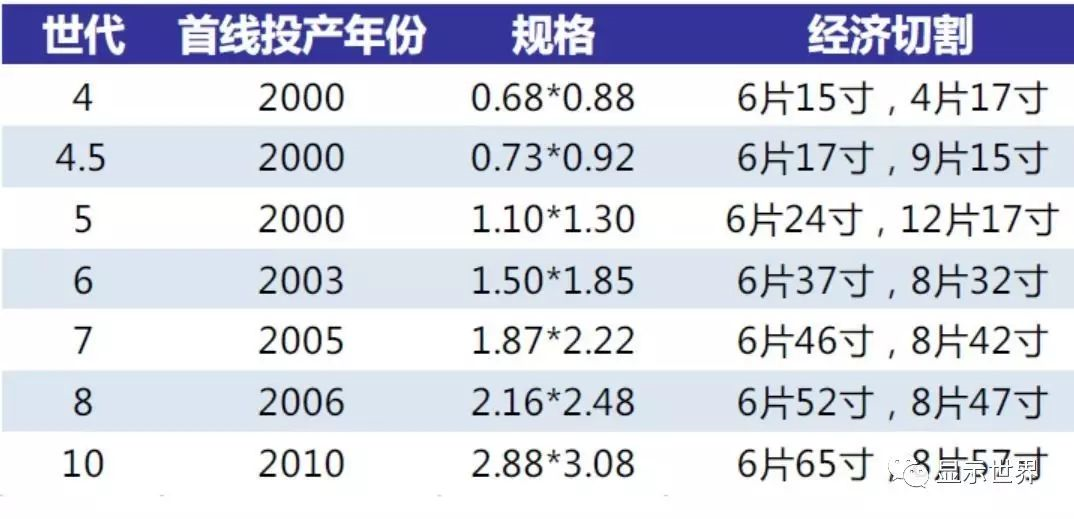
The development trend of substrate glass is higher generation and thinner
As it needs to be matched with the downstream panel factory, the production line of glass substrate is divided into generation lines according to the output glass area. The larger the area is, the higher the generation line is. Now the highest generation line in production is 10 generation line, with the size reaching 2880x3130mm. The development of the production line of panel to the higher generation line determines the same development trend of the production line of substrate. At present, the international glass giants of substrate have put their focus on Transfer to the construction of high generation line, the middle and low generation line will no longer open new capacity.
Evolution of generation line of substrate glass (specification unit: m)
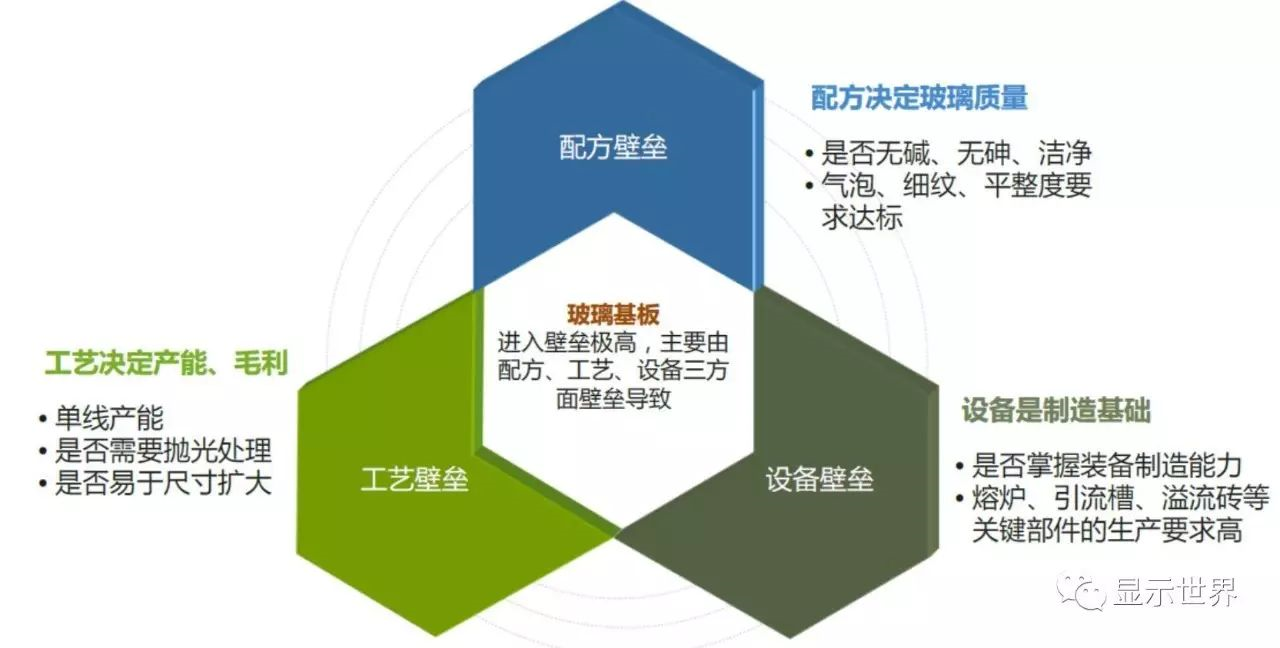
Technology, formula and equipment constitute three technical barriers of substrate glass industry
Substrate glass seems to be easy, as if it only needs to be thin, flat and clean enough, but in fact, the technical barriers are very high. The technical barriers of substrate glass manufacturing are mainly reflected in three aspects:
The first one is technological barrier: substrate glass for TFT-LCD has electronic requirements for glass surface flatness and impurity content, which can not be met by using general float process. After using the rear section for grinding and polishing, new surface impurities may be introduced due to media contact. At present, only Asahi has successfully used float process to manufacture substrate glass, which is the mainstream process of substrate glass It is still the overflow melting process, and the overflow melting process barrier is higher than the float process, so it is difficult to accurately adjust the temperature, flow rate and other parameters.
The second is formula barrier: This is the core barrier and the key technical part for the giants like Corning to monopolize the substrate industry. The overflow melting method needs the correct glass liquid formula to form stably, and the glass liquid formula also affects the optical and chemical properties of the substrate glass. In addition, arsenic oxide, as a chemical clarifier, is used in the traditional substrate glass manufacturing formula to accelerate the discharge of bubbles in the molten glass, but arsenic is a toxic metal, which does not meet the environmental protection requirements of some countries and regions. Arsenic containing glass The development of glass in export and downstream customers will be limited, and other methods must be used to eliminate bubbles when using arsenic free formula, so the technical difficulty will increase. In short, the formula is the core technology of substrate glass manufacturing, which is related to the yield of substrate glass products.
The third is equipment barrier: take overflow melting method as an example, because the production equipment is basically independently developed and produced by glass manufacturers, it is difficult for new entrants to buy off the shelf equipment in the market, so they need to redesign and make production equipment. In addition, due to the high production requirements of key components such as furnaces, drainage channels, overflow bricks, and so on, the non-compliance of some accuracy and characteristics will directly affect the yield of the final product, so there are also great barriers in the production of substrate glass production equipment.
Three barriers to entry of substrate glass industry
The entry barrier of the substrate glass industry is very high, but it is relatively easy to exit, which is mainly reflected in the two aspects of low single line investment of the substrate glass production line and easy to be converted to cover plate.
Different from the investment of 10 billion yuan in a panel production line, the investment in the substrate glass production line is relatively small. The investment in a six generation substrate glass production line is about 700 million yuan, of which 200-300 million platinum investment can also be recovered after sale. Therefore, there is little financial pressure to exit.
Base plate glass manufacturer has the ability and power to make cover plate glass
Glass cover plate is a layer of strengthened glass plate which plays a protective role in the outermost layer of mobile phone, tablet, ultrabook and other touchable mobile terminals. Because the requirements of the cover glass on the surface flatness and thickness of the glass are not as high as that of the base plate, and alkali free glass is not needed, the manufacturing difficulty of the cover glass is lower than that of the base plate glass. It is not difficult to transfer the base plate glass production line to the cover plate glass production line, and the investment of strengthening treatment in the later section is not high, as long as the formula is mastered, the transformation can only take one month; but it is much more difficult to transfer the cover plate production line back to the base plate. In addition to changing the glass liquid formula, the furnace should eliminate the alkali pollution caused by the cover plate glass production, and also need to use the equipment with higher temperature resistanceThis process is technically difficult and time-consuming. The overall conversion period is more than three months, and there is not much practice in the industry.
Production line conversion of base plate glass and cover plate glass
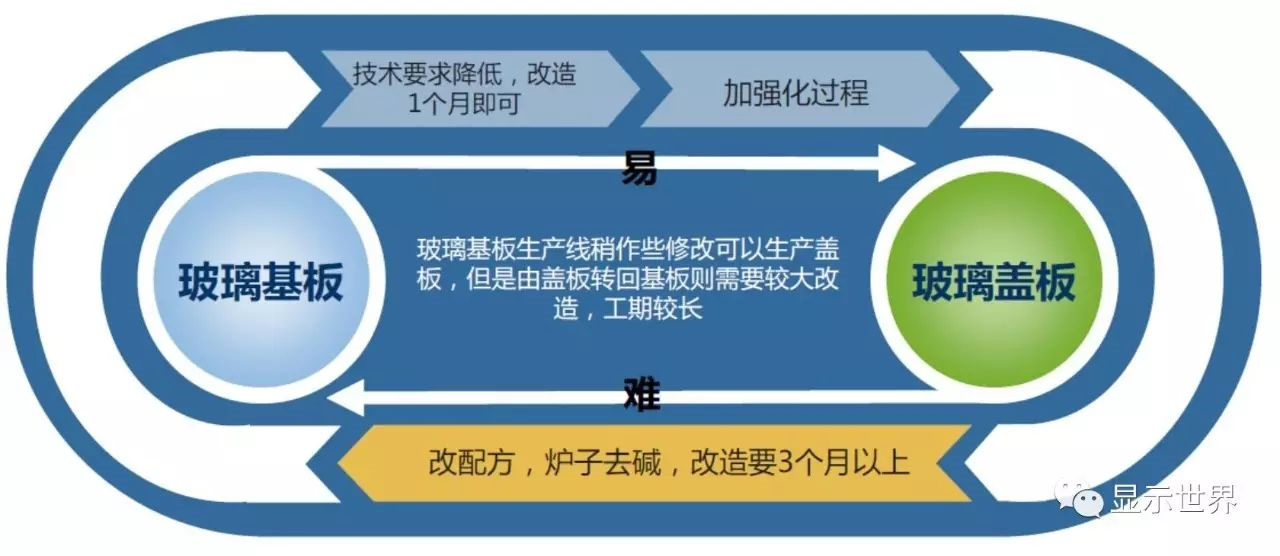
With the explosive growth of smart phones and tablet computers, the demand for cover glass also increased, and the supply was once tight. Among them, the "Gorilla" cover glass developed by Corning has been favored by many brand manufacturers, including apple, and has become the first choice for the cover glass of iPhone and other flagship mobile phones. With the hot sale of & ldquo; gorilla & rdquo; glass, and the profit of cover plate glass is stronger than that of base plate glass, Corning changed all the production lines in the United States to cover plate glass. In 2011 and 2012, Corning successively changed 10 production lines in Taiwan to cover plate.
From Corning's "gorilla road", it can be seen that the technical threshold for substrate glass manufacturers to switch to other glass products is not high because they occupy the high technical point, and the threshold is reflected in the formula. At present, the demand for cover plate is still rising. When the competition in the substrate industry intensifies, manufacturers withdraw from the substrate industry to switch to cover plate or even make more money. At present, Corning, the industry leader, is gradually transferring its low generation production line Make cover.
Taiwan kangningyuan substrate glass production line transformed into gorilla cover glass

Major manufacturers of cover glass in the world
Manufacturer
Country
Cover glass products
type
Launch time
Corelle
U.S.A
Gorilla
Overflow process high alumina glass
Two thousand and ten
Asahi
Japan
DragonTrail
Float high alumina glass
Two thousand and eleven
Electric nitrates
Japan
CX-01
Overflow process high alumina glass
Two thousand and eleven
Schott
Germany
Xensation
Float high alumina glass
Two thousand and eleven
Sun hung photoelectric
China
Panda King
Float high alumina glass
Two thousand and fourteen
Rainbow
China
Rainbow Keri
Overflow process high alumina glass
Two thousand and sixteen
Among the domestic glasses, Dongxu also introduced the high-strength and ultra-thin aluminosilicate glass with float process, and rainbow introduced the high aluminum cover plate glass with overflow process.
Xuhong photoelectric's high-strength ultra-thin touch screen glass production line, with an annual production scale of 7.8 million square meters, ranks the second in the world in terms of single line production capacity, second only to Japan's Asahi.
Rainbow cg01 overflow pull-down 6 generations of high aluminum cover plate glass, with a capacity of 100000-120000m2 / month, a production specification of 1520x1497mm and a thickness of 0.5-1.0mm.
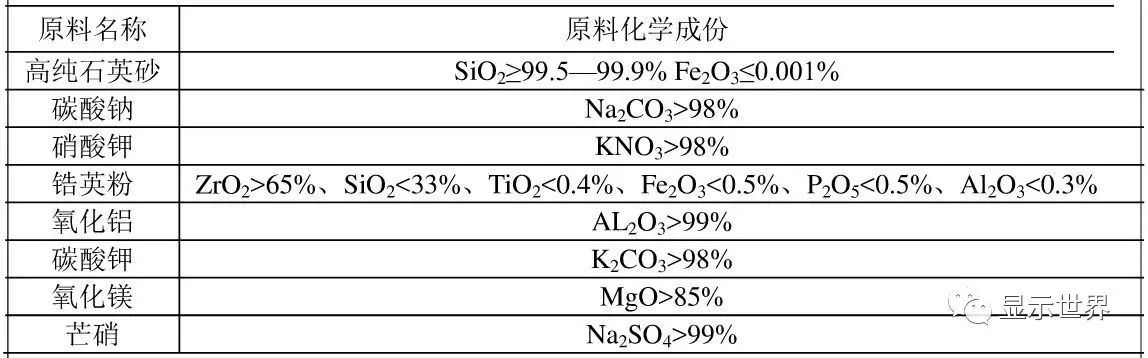
Main raw materials of high aluminum glass
The main raw materials of high alumina glass are: high purity quartz sand, sodium carbonate, potassium nitrate, zircon powder, alumina, potassium carbonate, magnesium oxide, mirabilite, etc.
Unlike panel manufacturing, which is a "money burning" industry, glass substrate is an industry that relies on technology for food. High barriers to entry result in good supply and demand, oligopoly, and high profit margin. Whoever can make qualified products can participate in the sharing of high profit cakes. The three barriers to glass substrate manufacturing block many entrants, Corning and Japan The oligopoly of glass manufacturers has been maintained for quite a long time.
Show the world's comprehensive self: Guangfa Securities, industrial information network, rainbow, Dongxu, etc.